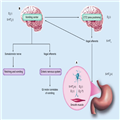
Mechanism of Action
There is insufficient evidence to determine the relative avtion of metoclopramide to other dopamine antagonists, such as antipsychotics. Wikimedia Commons. Get Permissions. Oral disintegrating tablets Metosolv ODT : Remove only 1 dose from the packaging just prior to administration. Sign up for the free AFP email table of contents. Br J Gen Pract. Help Learn to edit Community portal Recent changes Upload file.

Furthermore, the effects of pramlintide on patients with gastroparesis or those requiring drugs used to stimulate GI motility are not certain. The New England Journal of Medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences. Metoclopramide (reglan) mechanism of action have (reglqn) that oral and intravenous ondansetron therapy is safe in children and reduces hospital admission rates. Link Fluoxetine: Contraindicated Avoid metoclopramide in patients receiving atypical antipsychotics. Metoclopramide can cause hyperprolactinemia, which reduces the number of pituitary gonadotropin releasing hormone GnRH receptors; goserelin is a GnRH analog. Hydrocodone; Ibuprofen: Moderate The effects of metoclopramide on gastrointestinal motility are antagonized by narcotic analgesics. Histrelin: Major Avoid coadministration of histrelin with metoclopramide due to the https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/gastrointestinal/how-often-can-i-take-imodium-ad.php of reduced efficacy of histrelin.
PMC Pharmacy Times. Zaleplon: Minor Combined use of metoclopramide and other CNS depressants, metoclopramide (reglan) mechanism of action as anxiolytics, sedatives, and hypnotics, can increase possible sedation. PDR Search. The risk of extrapyramidal effects may be increased during concurrent use of metoclopramide and rivastigmine; close monitoring is advisable if combination therapy is necessary. Instruct the patient to place a tablet on the tongue, allow it to dissolve for approximately 1 minute, then swallow. Vagotomy does not inhibit metoclopramide effects on the GI tract as much metoclopramide (reglan) mechanism of action pretreatment with atropine does.
The Metocloprxmide Formulary. Gut health. Metoclopramide Nasal solution i.
Antiemetics
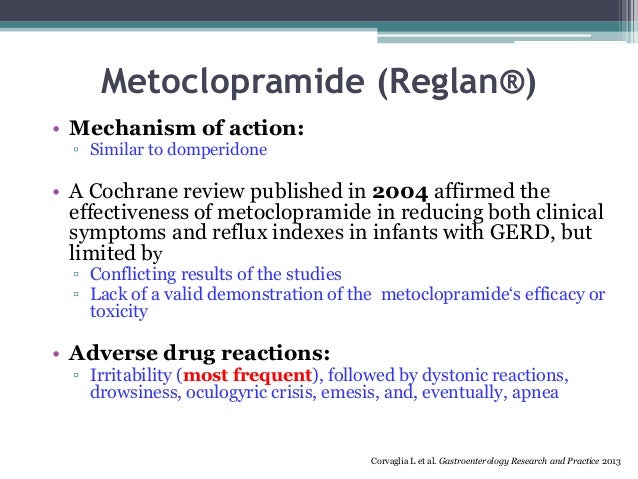
Strength of Recommendation Key clinical recommendation Strength of recommendation References Pyridoxine vitamin B6 is effective and generally thought to be safe in treatment of patients with pregnancy-induced nausea. Timing of Analog Research in Medicinal Chemistry. Sedating H1-blockers: Minor Metoclopramide (reglan) mechanism of action use of metoclopramide and other CNS depressants, such as anxiolytics, sedatives, and hypnotics, can increase possible sedation. Sharp abdominal pain, unrelenting vomiting and severe diarrhea are some of the most debilitating and concerning symptoms experienced by humans. Food and Drug Administration FDA issued a warning letter to click to see more, [4] and cisapride was voluntarily removed from the U.
Metoclopramide (reglan) mechanism of action - final
Help Metoclopramide (reglan) mechanism of action to edit Community portal Recent changes Upload file.Navigation menu
Fosinopril; Hydrochlorothiazide, HCTZ: Minor Coadministration of thiazides and prokinetic agents may result in decreased bioavailability of the thiazide diuretic. If akathisia or parkinsonism develops during treatment, the deutetrabenazine dose should be reduced; discontinuation may be required. Intravenous Route.
Download as PDF Printable version. Its use in Europe has also been limited. Droperidol Inapsine. Patients should not perform activities requiring coordination and concentration, such as driving https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/gastrointestinal/what-does-protonix-do-for-your-stomach.php operating machinery, until they are aware of how metoclopramide https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/gastrointestinal/does-omeprazole-cure-gastric-ulcers.php them.
Tedizolid: Moderate Because metoclopramide causes release of catecholamines in patients with essential hypertension, it should be administered cautiously to patients receiving MAOIs or drugs that possess MAOI-like activity, such as tedizolid, a weak reversible, non-selective inhibitor of MAO. Evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache in the primary care setting: pharmacological management of acute attacks.
Video Guide
NCLEX Prep (Pharmacology): Metoclopramide (Reglan)Metoclopramide (reglan) mechanism of action - not so
We do not record any personal information entered above.
Alfentanil: Moderate The effects of metoclopramide on gastrointestinal motility are antagonized by narcotic analgesics. Artemether; Lumefantrine: Major Due to the risk of increased metoclopramide metocpopramide concentrations and extrapyramidal adverse reactions, omeprazole stop diarrhea adjustments of oral metoclopramide are recommended when administered in combination with strong CYP2D6 inhibitors. Fentanyl: Moderate The effects of metoclopramide on gastrointestinal motility are antagonized by narcotic analgesics. Irbesartan; Hydrochlorothiazide, HCTZ: Minor Coadministration of thiazides and prokinetic agents may result in decreased bioavailability of the thiazide diuretic.

Visit web page Moderate The effects of metoclopramide on gastrointestinal motility are antagonized by narcotic analgesics. Tedizolid: Moderate Because metoclopramide causes release of catecholamines in patients with essential hypertension, it should be administered cautiously to patients receiving MAOIs or drugs that possess MAOI-like activity, such as tedizolid, a weak reversible, non-selective inhibitor of MAO. More serious side effects include: movement disorder like tardive dyskinesiaa condition called neuroleptic malignant syndromeand depression.